7.2 External Routers
The External router can be used in the following two ways:
- For routing calls and SMS, where the External Routing Machine (ERM server) partially replaces or complements the internal routing mechanisms of the 2N® NetStar PBX. Based on a call/SMS routing request, a query is sent to the ERM server. If a matching record is found in the ERM database table, the ERM server returns a response specifying a parameter for further call or SMS routing in the External router.
- For assigning names, where the ERM server is used as an external phone directory. Based on a CLIP-name assignment request, the PBX sends a query to the ERM server. If a matching record is found in the ERM phone directory, the ERM server returns the calling subscriber's name.
The DB connectors, used for setting the ERM server communication, are inseparable part of the external routers. Refer to Network – DB connectors for details.
The Routing – External routers menu consists of two windows: the list of created external routers is to the left and external router configuration to the right. The context menu displayed in the left part offers the following options:
- Add – open a router adding window and enter the router name.
- Delete – delete the selected router. This deletion automatically removes all database links to this object.
- Delete all – delete all routers in the menu. You will be asked to confirm the action before deleting.
- Rename – rename the selected router. If you enter an existing name, you will be warned and no change will be made.
- Add router group – add a group of routers.
- Add router subgroup – add a subgroup to the selected group of routers.
- Move to root level – move the selected object to a higher level beyond all created groups and subgroups.
- Move group content – move the group/subgroup content to another group/subgroup of routers.
- Copy router – make a copy of the selected router. Enter a new name. The router copy contains identical records as the original one (including the default destination).
- Show objects routed to router – activate a side window including listing of all objects that are routed to the selected router. This function helps you check the PBX routing settings.
- Expand all – expand the whole router group/subgroup structure easily.
- Collapse all – collapse the whole router group/subgroup structure easily.
Routing
Call/SMS routing via the External router is similar to standard routing. The only difference is the use of a Parameter. If the parameter value returned by the ERM server matches the value in any of the External router rows, routing to the set destination is executed.
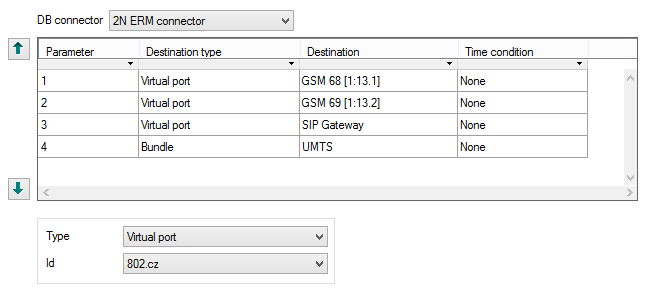
Figure: View of External Router Settings
- DB connector – select a DB connector to be used for communication with the ERM server. The External router cannot work without a DB connector assigned.
- Parameter – set a string of characters to be compared with the string returned buy the ERM server. Alphanumeric characters can be used.
- Destination type – set the type of destination to which the call shall be routed. All the PBX routing objects are available (if created) plus three options in which the destination is not obvious at first sight:
- Default – the call routing will jump to the next routing level if any. This option is primarily used for assigning objects to sets. Select this option to return the call from the router to the superior set and routing to the next item of the set follows.
- Disabled – terminate the call routing process. The calling subscriber gets the busy tone.
- Origin – return the modified number from the router to the original port.
- Destination – select a destination of the above selected type.
- Time condition – assign a time condition to each router row to make the row valid within the set time period only. Time conditions help you create rather sophisticated, time-dependent call routing schemes. Calls can thus be routed to different destinations at different times despite identical input conditions.
- Default destination – if no match is found in the Parameter with the value returned by the ERM server, the call is routed according to the Default destination settings (below the routing rule table):
- Type – set the destination type. All the PBX routing objects are available (if created).
- Id – select a destination of the selected type.
Names
The router rows are not applied in this mode and the call is routed directly to the External router default destination.