6.1 Global Parameters
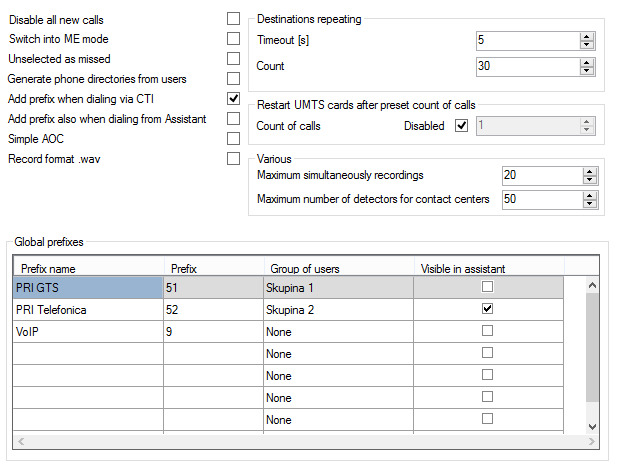
Disable all new calls
Tick off the parameter to switch the PBX into a mode in which no new calls can be made but active calls are not forcibly terminated. Trying to set up a call, the user fails being played a defined message. This function is useful for servicing purposes.
Switch on ME mode
Use this option to switch your PBX into the Mobility Extension mode, which is specifically used whenever the PBX is connected as a gateway between another PBX and various types of private or public networks. When this mode is active, all the Flash patterns and DTMF characters are sent directly to the opposite port of the PBX, which does not respond to them. This function has nothing to do with the Mobility Extension used for authorised external extensions!
Unselected as missed
This option sets the way of displaying missed calls. It refers to cases when an incoming call is routed to a group of extensions or to one user with multiple extensions and is answered by one of these extensions. If this option is not checked, missed calls are not displayed. If it is checked, missed calls are displayed at all extensions except for the one that has answered it.
Generate phone directories from users
Use this option to define the way of automatic generation of phone directories using the list of users or extensions in the Users – Phone directories – Group generated menu. If this option is checked off, the phone directory is filled with user names and respective internal numbers. If not, the phone directory is filled with extension names and respective numbers.
Repeat destinations
With firmware v. 2.7.0 and higher, you can repeatedly route a call to one and the same object. This is used, for example, for new routing in a bundle if the Repeat cyclically parameter is enabled.
- Timeout – define the time interval after which the same call can be routed to the selected object. If routed before the timeout end, the call is ignored by the PBX.
- Count – define the count of routing repetitions via one object for the given call. When this count is completed, call routing is terminated in the next routing attempt to this object.
Note
- An unduly low timeout value may result in a considerable PBX overload due to call deadlock.
Example:
Figure: View of Global Parameter Configuration Menu
Global prefixes
Global prefixes are primarily used for Analogue and VoIP virtual ports for easier dialling (CallBacks) even to public networks from the list of missed calls. The prefix is not added where the CLI has the Internal subtype. Assign the respective prefixes to the virtual ports using the Added prefix for external CLIP included on the Basic tab. Unlike the frequently used identification table, this option is applied close before departure to the selected port, i.e. after pairing with the telephone directory. It would be necessary to keep different phone directories for digital, analogue and SIP virtual ports if this option were not used.
- Add prefix when dialling via CTI – enable dialling prefixes also for CTI calls, i.e. calls from the Tray icon, Assistant and-or Communicator. In order to set up a call, the PBX checks the length of the called number against the Numbering plan length parameter in the Localisation menu. If the called number is longer, the prefix matching the calling user group is dialled.
- Add prefix also when dialling from Assistant – enable dialling prefixes also from the Assistant. The key fact for whether to enable or disable this item is whether or not the prefixes are included in the phone directories. If so, do not check this option off to avoid double prefix dialling. You can select this option only if the preceding one is enabled.
The meanings of the tab columns are as follows:
- Prefix name – define the prefix name to be used in other menus for identification.
- Prefix – define the prefix to precede the calling party identification.
- Group of users – define the group of users to use the given prefix. If no group is selected, the prefix is valid for all groups of the PBX.
- Visible in Assistant – display a prefix within the application. If it is not checked, the prefix is not available for use.
Example
Suppose a call is coming from a public network extension with the number 777123456. The call is routed through the PBX to the user Karel Furst, who belongs to user group 'Skupina 1'. His VoIP phone is registered to the SIP proxy, which has been assigned prefix PRI GTS (Figure 1) in the Added prefix for external CLIP parameter. If the number 777123456 is found in the phone book, the calling user name is sent to the terminal including the calling user number and the added prefix 51, i.e. 51777123456. To call this number back, the user Karel Furst can dial it directly from the list of missed calls (or received calls). The call is correctly and least-cost routed to the appropriate external port.
Billing
Simple AOC – this function helps you modify the billing rercords of the PBX. It allows you to simply distribute costs of such functions as call forwarding, Mobility Extension (bidirectionally) and CallBack. You are recommended to tick off the parameter before exporting data from the PBX at the latest. This simplification applies to CDRs created by firmware versions 3.0.0 and higher. The internal subscriber numbers are crucial for billing in these versions.
Recording
Record format .wav – select this option to store the call records in the .wav format. The default format is .alaw.
Miscellaneous
- Maximum simultaneous recordings – set the maximum count of calls to be recorded at the same time.
Caution
- Setting a value higher than 20 (default value) for the Maximum simultanous recordings may lead to a considerable load and malfunction of the PBX.
- Maximum number of detectors for contact centres – set the count of allocated DTMF detectors for the 2N® Contact Centre Solution.