4.1 States and Logs
States
This menu provides information on all 2N® OfficeRoute devices, registered VoIP extensions, calls and tariff metering states.
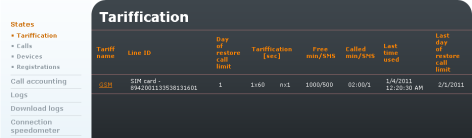
Tariff Metering
The list of available tariffs and usage of free minutes/SMS are displayed. Click on in the right-hand bottom corner to restore the calling and SMS limit.
Figure 4.1: States Tariffication
- Tariff name – Name of the tariff created.
- Line ID – Line for which the tariff has been created.
- Call limit restoring day – Day in a month on which called minute counters are reset.
- Tariffication – Applicable tariffication rule.
- Free min/SMS – Count of available free minutes and SMS.
- Called min/SMS – Count of used minutes and SMS.
- Last time used – Date and time of the last call or SMS.
- Last call limit restoring day – Date of the last minute and SMS limit restoring.
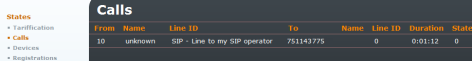
Calls
Information on current calls.
Figure 4.2: States - Calls
The columns include:
- From – Calling number.
- Name – Calling line name. It is completed only if this function is supported by the call-initiating IP telephone.
- Line ID – Line via which the call came to the gateway.
- To – Called number.
- Name – Called line name. It is completed only if this function is supported by the call-initiating IP telephone.
- Line ID – Line via which the call left the gateway.
- Duration – Call duration time.
- State – Connection status.
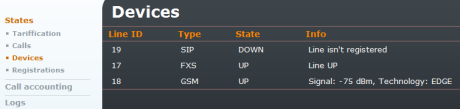
Devices
Signal strength and registration status with respect to external proxies.
Figure 4.3: States - Devices
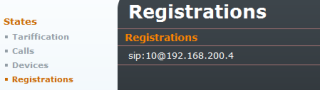
Registrations
Information on registered users.
Figure 4.4: States - Registrations
Call Accounting
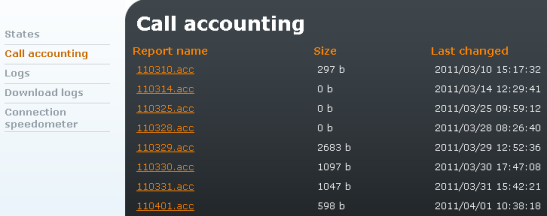
Provides detailed records on calls to mobile networks. The records on accomplished calls are saved into files in the text format. The file that the gateway currently saves call data into is called 'current.acc'. At the end of a predefined period of time, the file is renamed automatically and the gateway starts saving new call records into an empty file. The names of the closed files correspond with the respective period of time.
To display the list of saved call data files open the Call accounting menu in the States and Logs tags.
Figure 4.5: Call Accounting
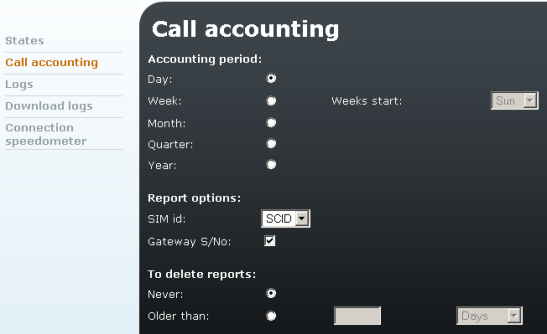
Using the icon it is possible to set the period of accounting reports, chose type of data contained in the CDR and set rules for deleting old CDR files.
Figure 4.6: Call Accounting - modify
- Accounting period – Select the period of accounting reports. In the case of a weekly report it is possible to specify the first day of report.
- Report options – Select items included in CDR:
- SIM Id – Select the type of SIM Id displayed in the CDR - SCID, CIMI or none.
- Gateway Serial No – If checked, each CDR will include the serial number of the gateway.
- To delete report – Specify a rule for deleting old CDR files.
Each file row corresponds to one call. For an example of a record see below.
| ** 30.03.05/08:35:57 O-OK CAU-000 gsm/1 0:08 000:10 123456789 +420602123456 4444 8942020390514319884 |
The record consists of fields separated with spaces
**– introductory sequence of the record.
- 30.03.05/08:35:57 – Date and time of call arrival in 2N® OfficeRoute.
- O-OK – Call type and status. The character before the hyphen indicates the call direction: 'I' represents calling from and 'O' calling to the GSM network. The two characters following the hyphen indicate how the call was cleared: 'OK' means correctly and 'FD' means disconnection due to error.
- CAU-000 – Call clearing code (error). The following options are available:
Code | Meaning |
CAU-000 | Normal call clearing |
CAU-001 | Internal protocol stack error |
CAU-002 | Protocol error |
CAU-003 | Alternative service |
CAU-004 | No free circuit |
CAU-005 | User busy |
CAU-006 | Call rejected |
CAU-007 | User not responding |
- gsm/1 – Module number via which the call was made.
- 0:08 – Call setup time. Time between call reception by the gateway until the called user's answer.
- 000:10 – Call duration (from the moment of the called user's answer).
- 123456789 – 2N® OfficeRoute identifier – serial number (optional).
- +420602123456 – Called number.
- 4444 – Calling number.
- 8942020390514319884 – SIM card identifier.
Logs
Events that come into being during the gateway operation are recorded in operation journals for subsequent error analysis purposes. The events are divided into five groups and saved into separate files
- Debug – Extended information used for development/diagnostic purposes.
- GSM AT – Gateway - GSM module communication record. This journal includes all AT commands sent to the GSM modules by the gateway and responses sent back.
- Data connection – Logging of communication between the module and the network between data connection.
- Warning – Events that should not occur normally but their presence has no effect on the gateway behaviour.
- Error – Errors that limit or jeopardise the gateway function. Their occurrence usually signals an approaching fatal error.
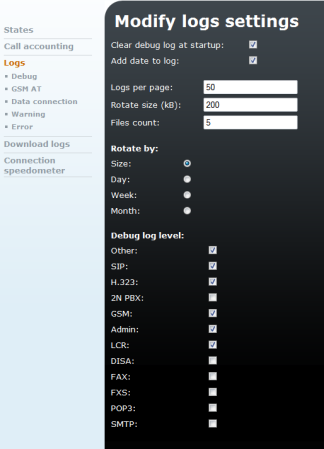
Figure 4.7: Logs - Settings
The form in Fig. 4.7 contains the following fields:
- Clear debug log at start-up – Define whether or not the tuning journal file should be deleted automatically upon the gateway power up.
- Add date to log – Define whether or not the gateway should add a timestamp to the events recorded.
- Logs per page – Number of lines to be displayed at the same time on one journal page.
- Rotate size (kB) – If the Rotating criterion is set in the Size (see below), the journal files shall be 'rotated off' whenever the defined size is exceeded (in kilobytes).
- Files count – Maximum number of 'rotated-off' files of each type that are stored in the gateway memory. The earlier ones are deleted automatically.
- Rotate by – Rotation criterion. The journal files are closed and renamed when a certain condition is satisfied and a new file is used for event recording. The files can be closed at the end of a defined period of time (day, week, or month) or when the specified size is achieved.
- Debug log level – Define which tuning record categories shall be recorded.
Download Logs
The viewing of the logs using a web browser as described in the preceding subsection is ineffective for complicated retrieval of events that happened in the distant past. In this case, it is more advantageous to download the journal files to your PC and view them using more sophisticated tools.
To download packed log files click on Download.
Figure 4.8: Download Logs
Connection Speedometer
In this section you can check your uploading and downloading speed. For more details refer to Subs. 3.4 – Network Settings.